Friday, April 11, 2014
The Heartbleed Bug - OpenSSL
Monday, October 21, 2013
HttpLog- Unique HTTP request Logger,HTTP URL Logger, HTTP Request Logger Appliance with Full URL Log.
HTTP URL Logger, HTTP Request Logger Appliance with Full URL Log.
Thursday, August 8, 2013
How to Fix Windows 8's Biggest Annoyances (and Make It More Like Windows 7)
How to Fix Windows 8's Biggest problems (and Make It More Like Windows 7)
Windows 8 has some awesome new features, but it also has its fair share of annoyances. Here's how to fix all of those problems, from bringing back missing features like the Start menu to fixing new problems like a dumbed-down Windows Explorer.
Bring Back the Start Menu
Look, we like Windows 8. It has some really cool stuff going for it, and most of the complaints surrounding it are misguided. However, there are a few annoyances that really need fixing. Instead of sticking with Windows 7 and missing out on Windows 8's improvements, we're going to show you how to get the best of both worlds.
Alternatively, you can use the free Classic Shell replacement, which is a tad more complicated but also more configurable than Start8. You have a lot more control over what your Start menu looks like, and can even tweak how the Search box works. When you install, you'll have the choice of installing just the Start menu or installing add-ons for Windows Explorer, Internet Explorer, and other programs too (more about this in a bit).The new Start screen isn't all that bad, but if you want the comfort of your old Start menu, it'sreally easy to bring back. Start8 is our favorite Start menu replacement, bringing a customizable start menu that fits in really well with Windows 8's new features and aesthetic. It's $5, but it's well worth the price and insanely easy to set up.
Get Rid of the Start Screen, Hot Corners, and More
If you really, really, really hate the tiled interface, you can get rid of it entirely with the aforementioned Classic Shell. Right-click on your Start menu and head into the settings. Under the "Windows 8 Settings" tab, you can check a box to skip the Start screen at login, as well as disable the hot corners if they trip you up. Start8 will also let you bypass the start screen, though it can't disable anything else.
If you're using Start8 instead of Classic Shell but want to disable the other "Metro" features, you can do so with a $5 program called RetroUI. It's simple: you can choose to bypass the Windows 8 Start screen after login, bypass the Start screen after locking your computer, or go all-out and get rid of everything: the Start screen, the Charms bar, and hot corners. Make sure you install Start8 first, or you'll have a lot of trouble opening programs and shutting down your computer since you won't have any of those functions available.
You can also disable the lock screen using Group Policy editor, if you so desire.
Customize the Ribbon-ified Windows Explorer
The new Windows Explorer has some cool features, but not everyone's a fan of the Ribbon interface. If that sounds like you, you have a few options for improving Explorer.
Classic Shell adds a new toolbar to Windows Explorer with small, simple buttons that you can customize to your heart's content. It isn't quite the same as having the old dropdown menus, but it's much simpler than the new Ribbon interface, and lets you add only the functions you'll actually use, which is nice. If you don't see it after installing Classic Shell, head to View > Options, click the Classic Explorer Bar to enable it, then click the seashell icon in the new toolbar to customize it.
Play DVDs for Free
However, if you prefer a more traditional file explorer with dropdown menus, you're better off with a full Explorer replacement likeXplorer2. Not only will it give you all your advanced menus back, but you'll get tabs, two-pane browsing, tons of keyboard shortcuts, and a fantastic search feature. It won't be quite as pretty as the new Windows Explorer, but if you long for traditional menus rather than the new Ribbon, this is your best bet.
Bad news, movie buffs: DVD playback is gone in Windows 8. Even if you download thecurrently-free Windows Media Center, it'll only allow you to play DVDs in Media Center—not in regular desktop programs like Windows Media Player.
If you want to play DVDs in Windows Media Player, it directs you to the Windows Store where you can buy an add-on for DVD support. Unless you really want to use WMP, don't waste your money—a program like VLC will play DVDs for free. Download it, install it, and forget about paying for DVD playback.
Bring Back the Confirmation Box When Deleting Files
In Windows 8, when you delete a file, it no longer asks you whether you're sure—it just sends the file right to the Recycle Bin. This was an option in Windows 7 as well, but it wasn't the default—and if you'd rather have that extra safety net, you can easily bring the confirmation dialog back. Just right-click on the Recycle Bin, choose Properties, and check the "Display Delete Confirmation Dialog" box.
Show the Desktop with a Hidden Button
Remember Aero Peek, the feature that let you hover over the edge of the taskbar to show your desktop? That's still around in Windows 8, but you have to enable it first. Right-click on the taskbar, choose Properties, and under the Taskbar tab check "Use Peek to Preview the Desktop." You won't see the button at the right edge of the taskbar like you did in Windows 7, but it's there—just hover your mouse over the area right of the clock and your windows will turn invisible again. You can also click this area to show the desktop instead of just peeking at it.
Replace Flip3D so You Can See Your Open Windows
Title image remixed from Yuri Arcurs (Shutterstock).Flip3D is also gone in Windows 8, but let's be honest: it wasn't that good to begin with. It was a nice piece of eye candy, but it wasn't exactly the most efficient way to see your open windows. There isn't a true replacement for Flip3D, but you can download a few programs that serve a similar purpose. Previously mentioned SmartFlip puts your windows in a wheel, letting you flip through them with whatever hotkey you want. Alternatively, you can download something like Switcher, which is more like OS X's Exposé, spreading your windows out into a grid when you press the desired hotkey. They won't bring back the eye candy of Flip3D, but they will serve the same purpose, and probably do it better.
Source: Lifehacker.com
Friday, August 2, 2013
Mikrotik Router - Step By Step Basic Configurations
Mikrotik Router - Step By Step Basic Configurations
This article explains how to configure Mikrotik device Router straight out of the box. It goes through the Winbox configuration utility and some of the basic setup procedures to turn your MikroTik device into a home or office wireless and wired router.
well In this tutorial we'll go through a step by step guide to make it as simple as possible to learn and implement these settings on your own routers.
These 4 Steps below are what we going to learn and setup for the beginning:
- Downloading and running winbox
- Setting an identity on the router
- Setting an IP address on the router
- Setting a password
STEP 1
Downloading and running winbox
Winbox is the graphical configuration utility designed for MikroTik RouterOS. It is a small application that can be downloaded from the MikroTik website athtttp://www.mikrotik.com Once you download winbox it can be run straight away, as no installation is required. It does however when running, setup a number of folders in your application data folder in order to save login data and plugins. This is transparent to the user but worthwhile to be aware, in order to diagnose problems and also understand the security implications of saving sensitive login information in the utility.
Setting an identity on the router
- Download the latest Winbox Configuration Tool under the Tools and Utilities section at http://www.mikrotik.com/download.html and place it to youdesktop.
- Double click on the Winbox icon on your desktop.
- Click on System menu item then on the Identy sub menu as in the image below.

- The Identity dialog will open as in image below. Remove the default "Mikrotik" value and replace it with something meaning full. Usually the location of the router combiened with its purpose acts as a suitable Identity for your router.

STEP 3
Setting an IP address on the router
To configure your Router IP Address
Click IP >> Addresses on the left menu in winbox as seen in image below.
This will open the Address list dialog window as seen below. Click on the red plus button to open the add IP address window.
When the New IP address dialog opens enter the address details select an interface to set the adress on and press apply and OK button.
Setting an IP address on the router
To configure your Router IP Address
Click IP >> Addresses on the left menu in winbox as seen in image below.
For information on what IP settings to use please see a basic tutorial in IP Networking. But just to explain one or two points about this dialog...
It is best to delete an address entirely instead of editing it, as I found that it a cleaner way of editing an address as to modify network or broadcast options can sometimes not apply 100% properly.
You have an option of entering the network and broadcast address explicitly in the boxes provided or is you prefer you can use the short slash notation and press the apply button, this will populate the broadcast and network boxes with the correct settings.
STEP 4
Setting a password for Mikrotik
This tutorial demonistrates how to set the password of the current Mikrotik Winbox user.
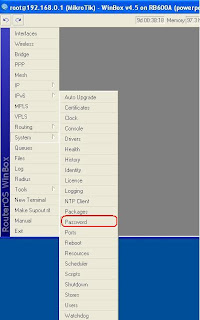
Click on the menu item as shown below
System >> Password
This will open the password dialog box as shown below.
Enter the old or current password followed by the new password that you wish to use.
If this is your first time logging into the router or the router is on factory settings the Old password box should be just left blank. As the default username and password is admin and no password.
Note:
This is how you set the password of the current Winbox user. To change other users you must go to system >> users menu item open that dialog and set the password for that particular user. You must have adequate user privileges to perform this action.
You have an option of entering the network and broadcast address explicitly in the boxes provided or is you prefer you can use the short slash notation and press the apply button, this will populate the broadcast and network boxes with the correct settings.
STEP 4
Setting a password for Mikrotik
This tutorial demonistrates how to set the password of the current Mikrotik Winbox user.
Click on the menu item as shown below
System >> Password
If this is your first time logging into the router or the router is on factory settings the Old password box should be just left blank. As the default username and password is admin and no password.
Note:
This is how you set the password of the current Winbox user. To change other users you must go to system >> users menu item open that dialog and set the password for that particular user. You must have adequate user privileges to perform this action.
setup PPPoE, NAT, DHCP server on Cisco Router
How to setup PPPoE, NAT, DHCP server on Cisco Router
Set up PPPoE, DHCP server, NAT in router cisco.
Figure:
Configuration file:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Current configuration : 1489 bytes
!
version 15.0
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
!
ip source-route
!
!
ip cef
!
!#########Create DHCP Server###########
ip dhcp pool InternalIP
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
dns-server 203.189.128.2 203.189.128.1
default-router 192.168.1.1
!######################################
!
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
!
license udi pid CISCO2821 sn FGL151311SM
username cisco password 0 cisco
!
!
!
!
!
!
!##############Enable PPPoE client on GigabitEthernet0/0##########
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no ip address
ip tcp adjust-mss 1452
duplex auto
speed auto
pppoe enable group global
pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
no cdp enable
!##################################################################
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
ip nat enable
ip virtual-reassembly
ip tcp adjust-mss 1452
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!###########setup PPPoE dialer 0 interface#################
interface Dialer0
description Connect to ONLINE
ip address negotiated
ip mtu 1454
ip nat outside
ip nat enable
ip virtual-reassembly
encapsulation ppp
ip tcp adjust-mss 1452
dialer pool 1
dialer-group 1
ppp authentication pap callin
ppp pap sent-username Your_Username password 0 Your_Password
no cdp enable
!###########################################################
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
no ip http server
###########Setup NAT########################
ip nat inside source list 99 interface Dialer0 overload
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer0
!
access-list 99 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
######################################
!
!
control-plane
!
!
line con 0
login local
line aux 0
!##########Enable Telnet Access#########################
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
password onlinecisco
login
!#######################################################
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
end
Figure:
Configuration file:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Current configuration : 1489 bytes
!
version 15.0
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
!
ip source-route
!
!
ip cef
!
!#########Create DHCP Server###########
ip dhcp pool InternalIP
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
dns-server 203.189.128.2 203.189.128.1
default-router 192.168.1.1
!######################################
!
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
!
license udi pid CISCO2821 sn FGL151311SM
username cisco password 0 cisco
!
!
!
!
!
!
!##############Enable PPPoE client on GigabitEthernet0/0##########
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no ip address
ip tcp adjust-mss 1452
duplex auto
speed auto
pppoe enable group global
pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
no cdp enable
!##################################################################
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
ip nat enable
ip virtual-reassembly
ip tcp adjust-mss 1452
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!###########setup PPPoE dialer 0 interface#################
interface Dialer0
description Connect to ONLINE
ip address negotiated
ip mtu 1454
ip nat outside
ip nat enable
ip virtual-reassembly
encapsulation ppp
ip tcp adjust-mss 1452
dialer pool 1
dialer-group 1
ppp authentication pap callin
ppp pap sent-username Your_Username password 0 Your_Password
no cdp enable
!###########################################################
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
no ip http server
###########Setup NAT########################
ip nat inside source list 99 interface Dialer0 overload
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer0
!
access-list 99 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
######################################
!
!
control-plane
!
!
line con 0
login local
line aux 0
!##########Enable Telnet Access#########################
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
password onlinecisco
login
!#######################################################
!
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
end
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)